In the post-pandemic era, innovation is more critical than ever before. Companies that are more innovative than their competitors survive the crisis, but they are also thriving in its midst.
That some of the world’s leading brands (such as GE and Apple) have quickly adopted the Design Thinking approach is no surprise. Design Thinking integrates innovative techniques to problem-solving with cutting-edge technologies and focuses on the future. Become a master in Design Thinking with the best Design Thinking certification.
Contents
What is design thinking?
IDEO, a global consulting firm based in Palo Alto, California, created Design Thinking as a method. Understanding the user, redefining challenges and challenging assumptions are all part of this iterative user-centric process that tries to develop new strategies and solutions.
As a result, design thinking pushes firms to focus on the people they are creating for, leading to better goods, services, and internal processes. It also makes it possible for people who aren’t designers to employ innovative approaches to a wide range of problems. Taking action and asking the correct questions are the first steps in the process. There are easy mentality modifications and fresh approaches to solving difficulties that you can adopt.
What is the significance of design thinking?
Organizations may create long-term value for their customers by employing design thinking. You can use this method in a variety of complex systems, not just design systems:
It aims to meet a specific human need
Teams can identify previously unidentified pain sites in customers using an observational, human-centric approach. Customers may not even be aware of these previously unknown points of suffering. Design thinking may suggest remedies as soon as those pain spots have been discovered.
Addresses ambiguous or complex issues
Consumers often don’t know or can’t express their problems. But with diligent observation, one may detect problems based on actual consumer behavior rather than just working off preconceived notions of the consumer. It clarifies unclear issues and helps find answers.
Encourages the development of more creative solutions
It’s hard for people to beg for things that don’t exist yet since they can’t imagine things that aren’t thought to be feasible. Using design thinking can help uncover some of these previously undisclosed pain issues. You can solve problems like this by using an iterative approach.
Increases the speed and efficiency of an organization’s operations
Design thinking prefers to create prototypes and then test them to evaluate their success rather than studying an issue.
How does Design Thinking work?
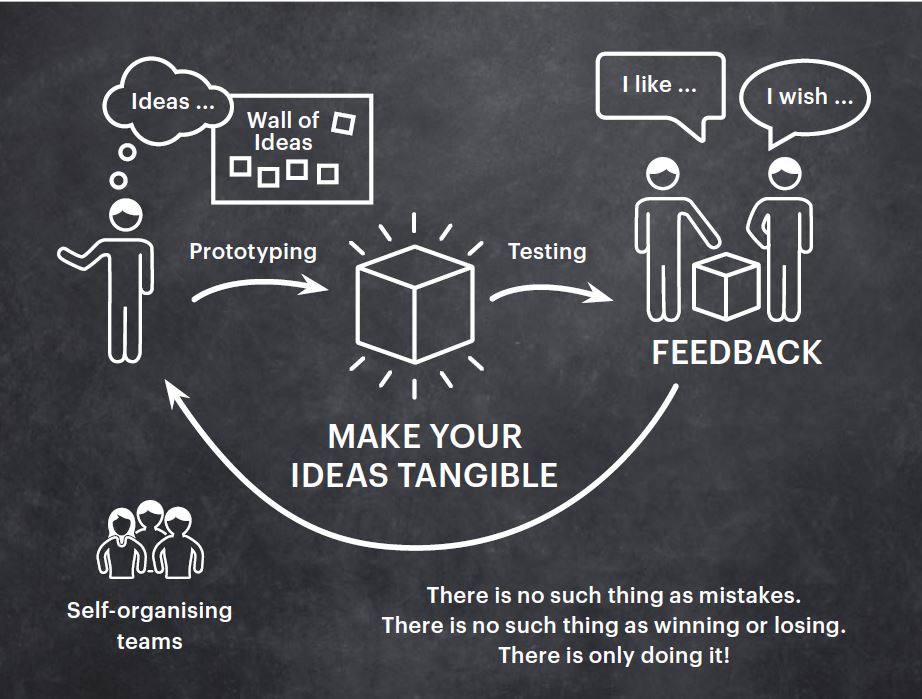
According to the Hasso-Plattner Institute of Design at Stanford (also known as the d.school), you may break down the Design Thinking process into phases: empathize, define, conceive, prototype, and test.
How can Design Thinking help you?
Empathize
Design Thinking begins with empathy. The initial part of the process is spent getting to know the user and their goals. They are observing and interacting with individuals to understand them psychologically and emotionally. Assumptions are set aside to get genuine user insights at this phase. Find out how to create empathy here.
Define
The second level of Design Thinking is the problem definition. You’ll start to make sense of your empathize findings: what challenges and barriers are your users facing? What trends do you see? What is the primary user issue your team must address? Defining the problem will result in a clear problem statement.
After defining the issue, you can start brainstorming solutions and ideas, which gets us to step three.
Initiate new concepts
You may now begin brainstorming possible solutions with a firm grasp of your users’ needs and a crystal-clear comprehension of their problems. The brainstorming stage is a judgment-free zone for the third phase of the Design Thinking process!
Designers will hold ideation sessions to develop as many fresh perspectives and ideas as possible. Designs can employ various techniques to generate ideas, from brainstorming and mind mapping to bodystorming (roleplay scenarios) and provocation. This method encourages the designer to think in a radically lateral fashion by forcing them to question long-held beliefs and consider new possibilities.
Create a prototype
Experimentation and the creation of physical objects focus on Design Thinking’s fourth step. If you think of it as a scaled-down version of the product, a prototype is basically what you’re looking for. It is critical to evaluate each solution and identify any limitations or problems. At each level of prototype development, the proposed solutions are estimated based on how well they perform in prototype form.
Test
Prototyping is followed by user testing. However, this is rarely the conclusion of the Design Thinking process. As a result of the outcomes of the testing process, you may need to go back and revise the initial problem statement or come up with new ideas.
Benefits of Design Thinking in the workplace
As a designer, you help shape the products and experiences your company sells. Integrating Design Thinking into your business process may ensure that the goods you design are not just desired by clients but also financially viable.
So, check these few primary advantages of implementing Design Thinking at work:
- Reduces time-to-market: Combining Design Thinking with lean and agile can dramatically cut design and development time.
- Low costs and high ROI: Getting profitable products to market faster saves money. Teams using IBM’s Design Thinking approaches, for example, have computed an ROI of up to 300 percent.
- Increases consumer loyalty: Design Thinking ensures a user-centric strategy that increases long-term engagement and customer retention.
- Fosters innovation: Design Thinking encourages all stakeholders to look outside the box. It promotes a culture of innovation beyond the design team.
- Company-wide usage: Design Thinking isn’t just for designers. It promotes groupthink and cross-team collaboration. It also works for practically any team in any business.
https://www.youtube.com/embed/b0Q1XZp-YTo
The bottom line
Design Thinking is a revolution that helps your business thrive in an ever-changing technological environment. Things outside your company have affected your customers’ expectations. They will judge your next release not on how much it improves your product but on how it compares to your customers.